GDPR Employee Personal Data Protection Policy Template
Introduction
Since the introduction of the GDPR into the EU, the rights of employees have been expanded to include the protection of the personal data that is collected by their employer. On top of protecting their personal data, the employer is bound to explain to the employees exactly which of their data is collected, how it’s stored, what it’s used for and how and when it will be disposed of.
This explanation must be written in everyday language, shared in a publicly accessible forum and be a part of each employment contract.
Working with a template will result in a personal data protection blueprint that can be easily maintained and shared with the employees.
Scope and Purpose
The GDPR has raised the issue of the rights of people regarding their personal data in general and the employees’ rights in particular. The policy aims at giving the employees a centralized document which can be used as a reference point in case of any dispute and can guide them in understanding which of their personal data is being collected, how it’s being used and with whom it’s shared. The policy can also be used for audits, either internal or external.
The policy is there to provide awareness of the following areas -
1. Types of personal data: Explain to the employees which attributes of their personal data are collected and at which point they are collected.
2. What the data is used for: Outlines what the employer does with the data once it’s collected.
3. Who has access to the data: Details which data controllers have access to the data, either internal or external.
4. Data protection principles: Explains how the data is kept safe.
5. Data breaches: How the organization will react to any type of data breach of their employees’ personal data, and which type of notifications will be sent and when.
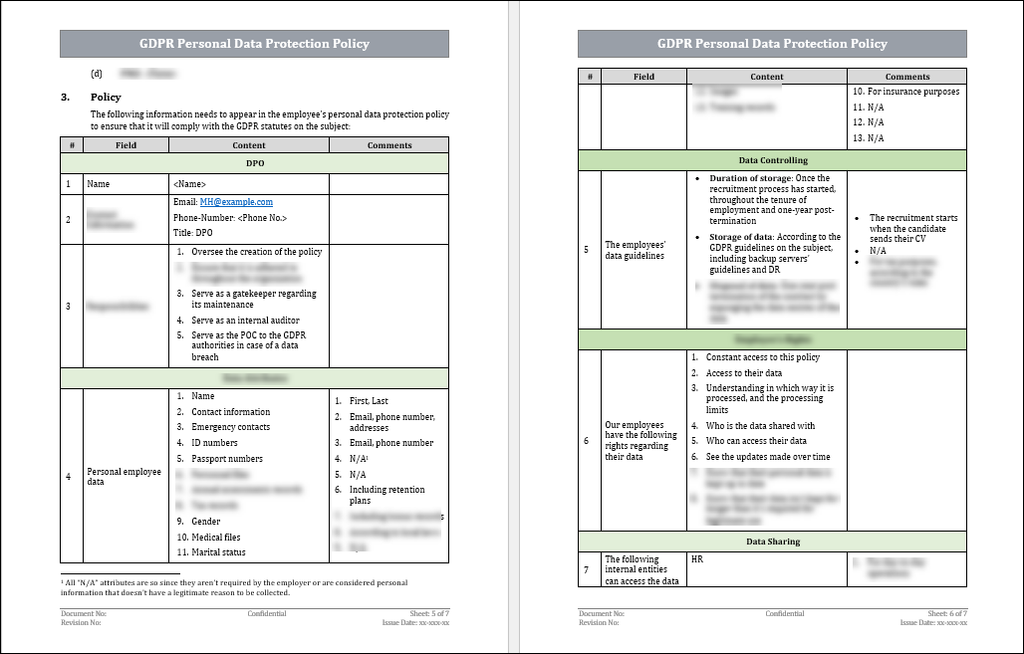
Required Fields In The Policy
The policy should include the following fields -
1. The details of the DPO who signs off on the policy once it’s created.
2. Data attributes: what constitutes personal data and which types are collected.
3. Data controlling: Defines for how long the data will be kept, how it will be stored, and when and how it will be disposed of.
4. The rights of the employees: Outlines the rights of each employee regarding the visibility of their personal data.
5. Sharing the data: Which entities inside and outside of the organization will be made privy to the data?
The Obligations of the Data Controller
1. Ensure that the personal data of the employees is being stored properly and according to the GDPR guidelines and is disposed of when no longer required.
2. Explains to the employees which data controllers (internal or external) have access to their data.
3. Facilitates keeping the policy up to date, sharing it with the employees and highlighting any changes that were made in the last version.
Term Definitions
What is a Data Controller?
An organization or person who determines the use of the collected personal data from the data subjects. The data controller owns the collected personal data, decides in which ways it will be processed and bears the sole responsibility for safekeeping it.
What is personal data?
Any type of unique data which relates to an individual data subject. This can include such information as Name, phone number, Email address, ID number, health records, political opinions, IP address, etc.
What is the processing of personal data?
Any act that is performed on the collected personal data of all the organizations’ data subjects. This may include such actions as storing the data, analyzing it in any way to extract insights or deleting it once it’s no longer required.
What is a data subject (also known as an end-user)?
Any person who created a unique username on the organization’s website, thus giving them the possibility of using that username to perform certain tasks and use features offered on the website.
What is a data breach?
Any intentional or unintentional security incident which involves the sharing of personal data with any unauthorized element. Sharing of personal data may include the viewing, copying, stealing, or altering of the personal data.
Who is the DPO?
The Data Protection Officer is the main stakeholder of the organization for all aspects of GDPR compliance. They are responsible for making sure that the GDPR guidelines are adhered to.
Key Takeaways / Conclusions
1. The DPO is responsible for overseeing the creation of the policy.
2. They are also responsible for ensuring that it is adhered to throughout the organization.
3. The policy should be maintained and periodically updated due to the changing laws and guidelines of the GDPR.
4. In case of a data breach, The DPO will serve as the point of contact for the GDPR authorities.


