SAP SOX Audit : Understanding Best Practices For a Successful SAP SOX Audit
Introduction to SAP SOX Audit
In today's business world, where security breaches and fraud are a constant threat, it is essential for companies to establish robust internal controls to safeguard their assets. One such control is the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX), which was enacted in the United States in response to major corporate scandals. SOX aims to ensure the accuracy and integrity of financial reporting, and it requires companies to comply with strict regulations.
Within the framework of SOX, an important aspect that organizations need to consider is the SAP SOX audit. SAP, short for Systems, Applications, and Products, is a world-renowned enterprise resource planning (ERP) software solution that enables businesses to streamline their operations and improve efficiency.
Importance of SAP SOX Audit in Business
First and foremost, the SAP SOX audit helps to identify and mitigate financial risks and control deficiencies within a company's SAP systems. By conducting regular audits, companies can identify any weaknesses or gaps in their internal controls that may lead to fraudulent activities, unauthorized transactions, or other financial misstatements. Identifying and rectifying these issues in a timely manner can prevent potential financial losses and reputational damage to the company.
Moreover, the SAP SOX audit helps instil investor confidence in the company's financial reporting process. By demonstrating compliance with SOX regulations, companies are assuring their investors that their financial statements are accurate and reliable. This, in turn, enhances the company's credibility and can attract more investments.
Another vital aspect of the SAP SOX audit is its contribution to improved operational efficiency. By assessing the effectiveness of internal controls and streamlining processes, companies can identify areas of improvement and eliminate unnecessary overheads. This can result in cost savings, enhanced productivity, and overall organizational efficiency.
Additionally, the SAP SOX audit helps companies stay on top of changing regulatory requirements. As laws and regulations evolve over time, it is essential for organizations to adapt and ensure compliance. By regularly conducting the SAP SOX audit, companies can identify any new requirements or changes in regulations and take necessary actions to align their SAP systems accordingly.
The SAP SOX audit is of paramount importance for businesses to comply with the Sarbanes-Oxley Act and maintain transparency, accountability, and integrity in their financial reporting.
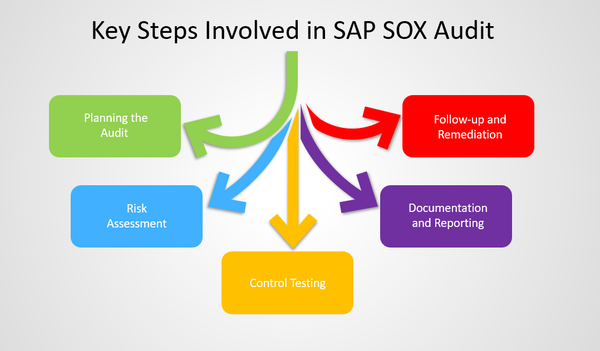
Key Steps Involved in SAP SOX Audit
The key steps involved in an SAP SOX Audit are as follows:
Step 1: Planning the Audit: The first crucial step in conducting an SAP SOX Audit is planning. This involves understanding the organization's business processes and identifying the key risks associated with them. The audit team needs to comprehend the SAP landscape, including the modules in use, customizations, and any third-party applications integrated with SAP. The audit plan should also include the scope, objectives, and timelines of the audit.
Step 2: Risk Assessment: Once the audit plan is in place, the next step is to perform a comprehensive risk assessment. The objective is to identify potential risks that could impact the integrity of financial reporting. This involves understanding the critical controls within the SAP landscape and assessing their design and operating effectiveness. The risk assessment should focus on key areas such as access controls, change management, segregation of duties, and data integrity.
Step 3: Control Testing: After identifying the risks, control testing is conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of controls in mitigating these risks. This involves reviewing the access controls, system configurations, and user provisioning processes within the SAP environment. The audit team selects a sample of control activities and performs detailed testing to ensure their adherence to the defined control objectives. Any control gaps or deficiencies identified during testing should be documented and remediated.
Step 4: Documentation and Reporting: The audit team then prepares the audit documentation, which includes all the findings, observations, and recommendations. This documentation serves as evidence of the audit work performed and is crucial for future reference and accountability. The audit report should clearly communicate the identified control weaknesses and provide recommendations for improvement. The report is shared with management and other stakeholders to drive corrective actions and ensure compliance with SOX requirements.
Step 5: Follow-up and Remediation: The final step in the SAP SOX Audit is the follow-up and remediation process. This involves tracking the progress of the remediation efforts and validating the implementation of corrective actions. The audit team collaborates with the business process owners and IT teams to ensure the identified control weaknesses are effectively addressed. Regular monitoring of remediation progress is vital to ensure sustainability of the internal controls and ongoing compliance with SOX requirements.
Best Practices for a Successful SAP SOX Audit
To achieve a successful SAP SOX audit, organizations must follow a set of best practices that will help them ensure the integrity and security of their financial data. Let's take a look at some of these best practices:
1. Clearly Define Roles and Responsibilities: The first step to a successful SAP SOX audit is to clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each individual involved in the audit process. Assigning specific tasks and accountabilities will help streamline the audit and ensure that all necessary areas are covered.
2. Document Key Controls: It is crucial to thoroughly document key controls in the SAP system. This includes controls related to user access, segregation of duties, and data integrity. Documenting these controls will provide auditors with a clear understanding of the organization's internal control framework.
3. Perform Regular Risk Assessments: Conducting regular risk assessments is an essential part of any SAP SOX audit. This will help identify potential risks and vulnerabilities within the system and allow organizations to implement necessary controls to mitigate these risks. By staying proactive and addressing risks before they become issues, organizations can enhance the success of their SAP SOX audit.
4. Monitor and Review Controls: It is important to continuously monitor and review controls within the SAP system. This will help identify any control failures or deviations in a timely manner. Regular monitoring and review will enable organizations to take corrective actions promptly, reducing the chances of non-compliance during the audit.
5. Implement Change Management Processes: Organizations should establish robust change management processes to ensure that any modifications or developments in the SAP system are properly documented and tested. This will help maintain the integrity and stability of the system, reducing the risk of non-compliance during an audit.
6. Engage Internal and External Auditors: Collaborating with both internal and external auditors is key to a successful SAP SOX audit. Internal auditors can provide valuable insights into the organization's control environment, while external auditors can bring an independent perspective and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the SAP SOX audit is an essential component of corporate governance, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting. This audit serves as a means to identify control weaknesses within SAP systems, which can pose significant risks to the organization's financial statements. By conducting this audit, companies can enhance their internal controls, mitigate financial risks, and provide investors with the confidence they need to make informed decisions.


