RACI For Service Design And Transition Template
Introduction
The RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) for Service Design and Transition Template is an important framework in IT Governance for defining roles and duties throughout the complex stages of service development and deployment. This template gives an organised way to identifying persons or groups accountable for carrying out specified activities, ensuring responsibility, encouraging collaboration through consultation, and preserving open communication by keeping relevant parties informed. Organisations who adopt the RACI framework within the context of Service Design and Transition can optimise their IT processes, improve project efficiency, and ultimately contribute to the seamless delivery of high-quality services.
Importance Of Effective Service Design And Transition
Effective Service Design and Transition are critical components of IT Governance, ensuring that IT services correspond with organisational objectives while conforming to established frameworks and standards. In IT Governance, service design is the blueprint for aligning IT services with business requirements and regulatory compliance. It enables the development of scalable, adaptive, and cost-effective services that may evolve in response to changing organisational needs. Transition planning, on the other hand, is critical for orchestrating the smooth introduction of these services, minimising disruptions, and optimising resource utilisation. Together, these phases help to develop a governance framework that not only reduces risks and guarantees compliance, but also promotes operational efficiency and strategic alignment.
By clarifying roles, responsibilities, and resource allocations, these phases enable governance teams to make informed decisions that prioritise service quality, security, and efficiency. As IT governance becomes more important to organisational performance, the ability to design and transition services successfully becomes critical to maintaining a strong and adaptable IT infrastructure. As a result, organisations can traverse the intricacies of today's digital ecosystem while proactively tackling obstacles and capitalising on possibilities for innovation and growth.
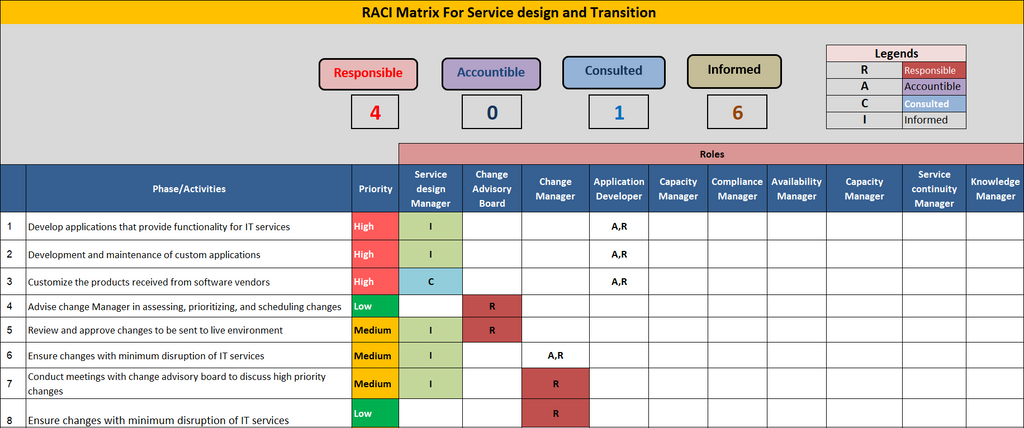
Responsibilities For Each RACI Category In Service Design
1. Responsible (R): The individual or team in charge of carrying out a given task or activity.
Responsibilities:
- Prepare precise design plans and specifications.
- Carry out the actions described in the service design phase.
- Collaborate with other stakeholders to collect the relevant information.
- Ensure that the design satisfies the specifications and standards.
2. Accountable (A): The individual is ultimately responsible for the success or failure of the endeavour. Only one 'A' should be allocated to each task.
Responsibilities:
- Approve the overall design and how it aligns with organisational goals.
- Ensure that the service design adheres to quality standards and regulatory requirements.
- Provide final design decisions and sign off on critical deliverables.
- Oversee the full-service design process, including its integration with overall organizational goals.
3. Consulted (C): Individuals or groups whose feedback is sought prior to making decisions or taking action.
Responsibilities:
- Provide subject area expertise for certain design aspects.
- Collaborate on design decisions, providing feedback and comments.
- Participate in design evaluation and discussion.
- Contribute to the overall design approach using their knowledge.
4. Informed (I): Individuals or groups who require regular updates on the task's progress and consequences but are not actively involved in its implementation.
Responsibilities:
- Get information on the status of service design initiatives.
- Stay informed about important choices and milestones.
- Be aware of any changes or modifications made during the design process.
- Provide feedback when needed, but their involvement is not necessary for decision-making.
Conclusion
The RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed) for Service Design and Transition Template is a cornerstone of IT Governance, offering a formal framework for orchestrating roles and duties during the essential stages of service development and deployment. This template not only allows for a systematic split of duties, but it also improves collaboration, accountability, and communication between important stakeholders. Organisations can navigate the complexities of IT service management with precision and efficiency by clearly defining who is responsible for carrying out specific activities, who is ultimately accountable for the success of the overall design, who needs to be consulted for their expertise, and who should be kept informed about progress and outcomes.


