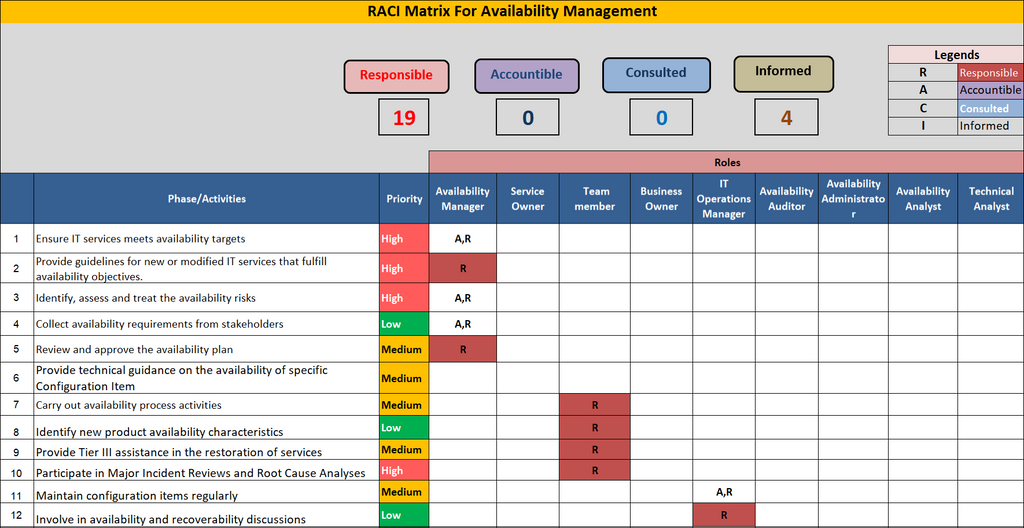
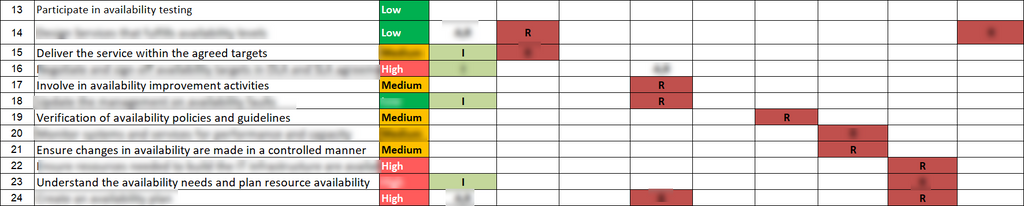
RACI For Availability Management Template
Introduction
The RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) for Availability
Management Template emerges as a strategic framework designed to bring clarity and efficiency to the orchestration of roles and responsibilities within this critical domain. This template acts as a guiding compass, delineating the specific functions and tasks associated with Availability Management while assigning distinct roles to individuals or groups. By fostering a structured approach, RACI not only streamlines decision-making processes but also enhances communication and accountability, thereby contributing to the robustness and resilience of IT systems. In this blog, we delve into the complexities of
this indispensable tool, exploring its nuances, applications, and best practices in the realm of Availability Management within the broader spectrum of IT Governance.
Importance Of Availability Management
In an era where businesses heavily rely on technology, downtime can lead to severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and diminished customer trust. Availability Management, as a fundamental component
of IT Governance is tasked with proactively ensuring that IT services are consistently available, reliable, and perform at optimal levels. By meticulously planning, monitoring, and addressing potential disruptions, Availability Management not only safeguards against the impact of service outages but also aligns IT infrastructure with business objectives, fostering a resilient and responsive organizational ecosystem.
Moreover, in the context of IT Governance, Availability Management contributes to the the overall efficiency of an organization by minimizing disruptions and enhancing the predictability of IT services. This, in turn, enables businesses to maintain a competitive edge in the digital landscape, meet regulatory compliance
requirements, and cultivate a robust IT infrastructure that can adapt to evolving technological landscapes. As IT Governance increasingly becomes a strategic priority for organizations, Availability Management emerges as a key
element, ensuring that technology remains an enabler rather than a hindrance to organizational success.
Customizing The RACI Matrix For Availability Management Template
Customizing the RACI matrix for Availability Management is a crucial step in tailoring this governance framework to the unique needs and intricacies of an organization's IT landscape.
Here's a breakdown of the process:
1. Identifying Specific Tasks And Activities:
- Begin by listing the key tasks and activities associated with Availability Management. This could include routine monitoring, incident response, capacity planning, and recovery planning.
- Clearly define the scope of each task to avoid ambiguity in role assignments.
2. Assigning Roles To Each RACI Category:
- Responsible (R): Identify the individuals or teams responsible for executing specific tasks. These are the hands-on contributors directly involved in the activity.
- Accountable (A): Designate the individual who is ultimately answerable for the success or failure of the task. This is often a single person with the authority to make final decisions.
- Consulted (C): Specify the individuals or groups that need to be consulted for their expertise or input before decisions are made or actions taken. These stakeholders may offer valuable insights.
- Informed (I): Determine the parties that should be kept informed of progress and outcomes without direct involvement in the execution.
3. Establishing Clear Communication Channels:
- Define effective communication channels for each RACI role. This ensures that information flows seamlessly among team members, preventing bottlenecks and misunderstandings.
- Leverage collaboration tools, project management platforms, or regular meetings to facilitate communication within and between RACI roles.
4. Periodic Review And Updates:
- Availability Management is dynamic, and IT landscapes evolve. Regularly review and update the RACI matrix to accommodate changes in technology, organizational structure, or business priorities.
- Solicit feedback from team members involved in each role to fine-tune the matrix for improved efficiency.
5. Integration With Other IT Governance Processes:
- Ensure alignment between the RACI matrix for Availability Management and other IT governance processes such as Incident Management, Change Management, and IT Service Continuity.
- Identify interdependencies and overlaps to streamline workflows and prevent conflicts.
6. Training And Awareness:
- Conduct training sessions to familiarize teams with their respective roles and responsibilities within the RACI matrix. This helps in building a shared understanding of the governance framework.
- Foster awareness about the importance of Availability Management and how each role contributes to the overall resilience of IT services.
Benefits Of Using RACI For Availability Management Template
1. Clarity In Roles And Responsibilities:
- Responsible (R): Clearly defines who is responsible for executing specific tasks related to Availability Management.
- Accountable (A): Designates the ultimate decision-maker, ensuring that there is a clear point of accountability for the overall success of Availability Management efforts.
2. Improved Communication:
- Consulted (C): Involves key stakeholders with relevant expertise in the decision-making process, fostering collaboration and drawing on a diverse range of insights.
- Informed (I): Keeps stakeholders informed about progress, outcomes, and changes, maintaining transparency and promoting a shared understanding of the Availability Management strategy.
3. Enhanced Decision-Making:
- Streamlines decision-making processes by providing a structured approach to involving relevant stakeholders in key decisions.
4. Risk Mitigation And Proactive Management:
- Clearly identifies who is responsible for monitoring and addressing potential risks to Availability, allowing for a proactive approach to risk management.
5. Efficient Resource Utilization:
- Avoids duplication of efforts by clearly assigning responsibilities, preventing unnecessary overlaps or gaps in tasks related to Availability Management.
6. Adaptability To Change:
- Facilitates easy adaptation to changes in the IT landscape by providing a structured framework for updating roles and responsibilities within the Availability Management process.
7. Continuous Improvement:
- Supports a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and updating the RACI matrix in response to feedback, changing circumstances or lessons learned.
8. Alignment With Business Objectives:
- Ensures that Availability Management activities are closely aligned with broader business objectives, contributing to the overall success of the organization.
Conclusion
The integration of the RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed) matrix into Availability Management within the broader scope of IT Governance offers a robust framework that significantly contributes to the resilience and efficiency of an organization's IT infrastructure. By providing clear delineation of roles and responsibilities, the RACI matrix minimizes ambiguity and enhances accountability, ensuring that tasks critical to Availability Management is executed with precision and purpose. The structured approach of the RACI matrix not only streamlines decision-making processes but also fosters effective communication among stakeholders.


