IT Governance Components, Process and Challenges
In today's rapidly evolving business landscape, Information Technology (IT) governance stands as a critical framework that ensures the effective and strategic management of IT resources within organizations. It serves as the linchpin aligning technological strategies with overarching business objectives, mitigating risks, optimizing resource utilization, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted aspects of IT governance, exploring its components, processes, and the prevalent challenges faced in its implementation.
Understanding IT Governance
Defining its Purpose
IT governance encapsulates the policies, procedures, and frameworks governing IT investments, operations, and decision-making processes within an organization. The fundamental purpose lies in harmonizing IT strategies with business goals, enhancing operational efficiency, mitigating risks, fostering innovation, and ensuring regulatory compliance. By achieving these objectives, IT governance becomes instrumental in shaping and supporting an organization's success in the competitive market landscape.
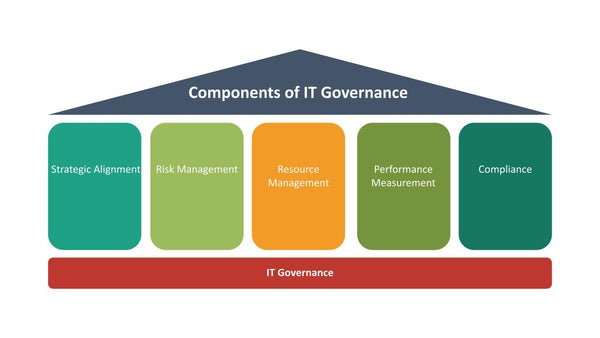
Components of IT Governance
- Strategic Alignment: This component revolves around ensuring that IT initiatives and investments are in sync with the broader business strategies. It involves defining clear goals and objectives that IT should achieve to contribute effectively to the organization's success.
- Risk Management: Managing IT-related risks is a pivotal component of IT governance. This includes identifying potential threats, implementing robust security measures, disaster recovery plans, and ensuring data integrity to safeguard against cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
- Resource Management: Efficient utilization of IT resources, including human capital, infrastructure, and financial assets, is crucial. Effective governance ensures optimal resource allocation to support business objectives while controlling costs.
- Performance Measurement: Establishing measurable KPIs and metrics to evaluate the effectiveness and efficiency of IT operations is essential. Regular assessments aid in identifying areas for improvement and opportunities for innovation.
- Compliance: Adherence to regulatory requirements, industry standards, and internal policies is integral. This component focuses on ensuring that IT practices and operations comply with relevant laws and regulations.
IT Governance Processes
- Strategic Planning
Strategic planning serves as the foundation for IT governance. It involves a thorough analysis of the organization's current IT landscape and aligning it with overarching business objectives. This process encompasses identifying technological needs, opportunities, and challenges that can impact the organization's growth. By understanding these factors, strategic planning guides the formulation of robust IT strategies. These strategies not only address current needs but also anticipate future requirements, ensuring that IT initiatives are aligned with the organization's long-term vision.
- Decision-making
Structured decision-making processes are crucial within IT governance. These processes incorporate comprehensive risk assessments, resource allocation strategies, and compliance considerations. By integrating these elements, organizations can make informed decisions that support business objectives while mitigating potential risks. The decision-making framework ensures that investments in IT projects and initiatives align with the organization's strategic goals. This approach fosters agility and adaptability, allowing organizations to respond effectively to changing market dynamics and technological advancements.
- Performance Monitoring and Assessment
Continuous monitoring and evaluation of IT performance against predefined Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are central to effective governance. This ongoing assessment ensures that IT activities remain aligned with organizational goals. By tracking metrics related to efficiency, effectiveness, security, and service delivery, organizations gain insights into areas that require improvement. This iterative process of evaluation enables timely adjustments and optimizations to enhance overall IT efficiency and effectiveness.
- Risk Management
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating IT-related risks is pivotal for safeguarding an organization's assets and ensuring business continuity. Proactive risk management involves evaluating vulnerabilities, implementing robust security measures, and devising contingency plans. With the evolving landscape of cyber threats, effective risk management strategies are crucial in protecting sensitive data and mitigating potential disruptions to business operations.
- Compliance Management
Ensuring adherence to applicable laws, regulations, and internal policies is a critical aspect of IT governance. Regular audits, assessments, and compliance checks are conducted to verify that IT operations comply with legal requirements and industry standards. Compliance management not only mitigates legal and reputational risks but also fosters a culture of accountability and responsibility within the organization.
Challenges in Implementing IT Governance
- Rapid Technological Evolution
The relentless pace of technological advancements presents an ongoing hurdle for organizations. Staying abreast of emerging technologies such as AI, IoT, and cloud computing while ensuring their integration into existing governance structures poses a substantial challenge. Implementing governance that adapts swiftly to these innovations, maintains security standards, and aligns with business goals requires continuous vigilance and agile strategies.
- Cybersecurity Threat Landscape
The ever-evolving threat landscape of cyberattacks presents a formidable challenge. Organizations face an array of sophisticated threats, including ransomware, phishing, and zero-day exploits. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures within the governance framework becomes a critical priority. Continuous updates, advanced security protocols, and employee education are essential to mitigate risks and safeguard sensitive data from breaches.
- Complexity at Scale
Large enterprises often grapple with the intricacies of managing governance frameworks across diverse systems, departments, and geographic locations. Coordinating governance practices uniformly while accommodating the specific needs and nuances of different business units can be exceptionally challenging. Achieving coherence and consistency in governance across the organization demands a concerted effort to streamline processes and communication channels.
- Resource Allocation Dilemmas
Balancing resource allocation poses a persistent challenge for organizations. Determining optimal resource allocation across IT initiatives, infrastructure upgrades, talent acquisition, and innovation endeavors requires careful strategic planning. Often, organizations face dilemmas in allocating resources between urgent security needs and long-term technological innovation, necessitating astute decision-making and trade-off analyses.
- Cultural Transformation
Implementing effective IT governance often necessitates a cultural shift within the organization. Resistance to change, lack of awareness, and varying levels of technological literacy among employees can impede the adoption and success of governance initiatives. Overcoming these cultural barriers requires proactive change management strategies, continuous education, and fostering a culture that values and embraces technological advancements.
Conclusion
IT governance serves as a cornerstone for organizations aiming to leverage technology for competitive advantage while effectively managing risks and resources. By understanding its components, processes, and the challenges involved, businesses can craft robust governance frameworks tailored to their unique needs. Overcoming these challenges demands a proactive approach, continuous assessment, and a commitment to aligning IT strategies with organizational objectives.
In the dynamic digital landscape, embracing adaptable and resilient IT governance practices is not just a necessity but a strategic imperative for organizations striving for sustainable growth and success.


