ISO 27001: 2022 Information Security Risk Register
As businesses increasingly rely on technology, a robust information security risk register becomes imperative. This document should comprehensively enumerate all potential threats to the organization's information security, along with the corresponding mitigation measures in place. By maintaining this document, companies can ensure they are well-prepared for unforeseen circumstances.
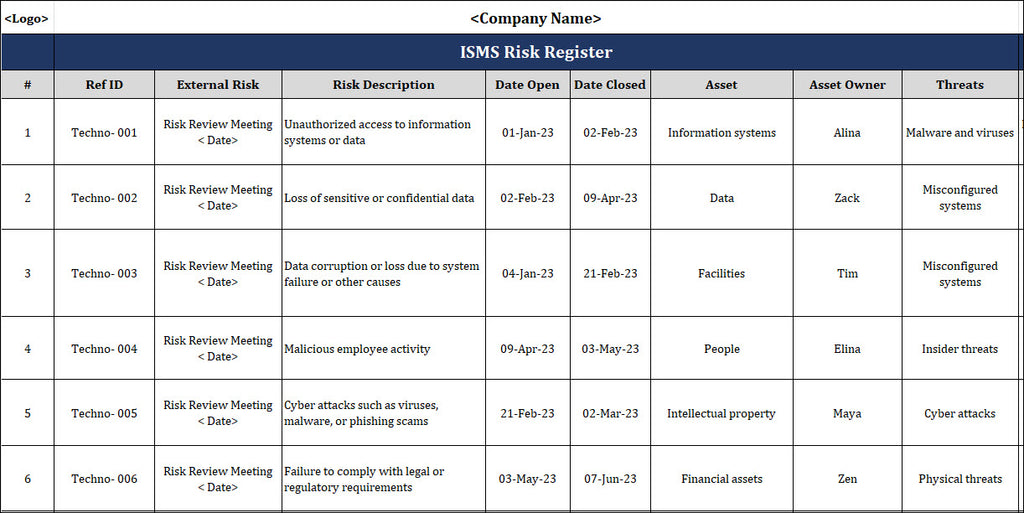
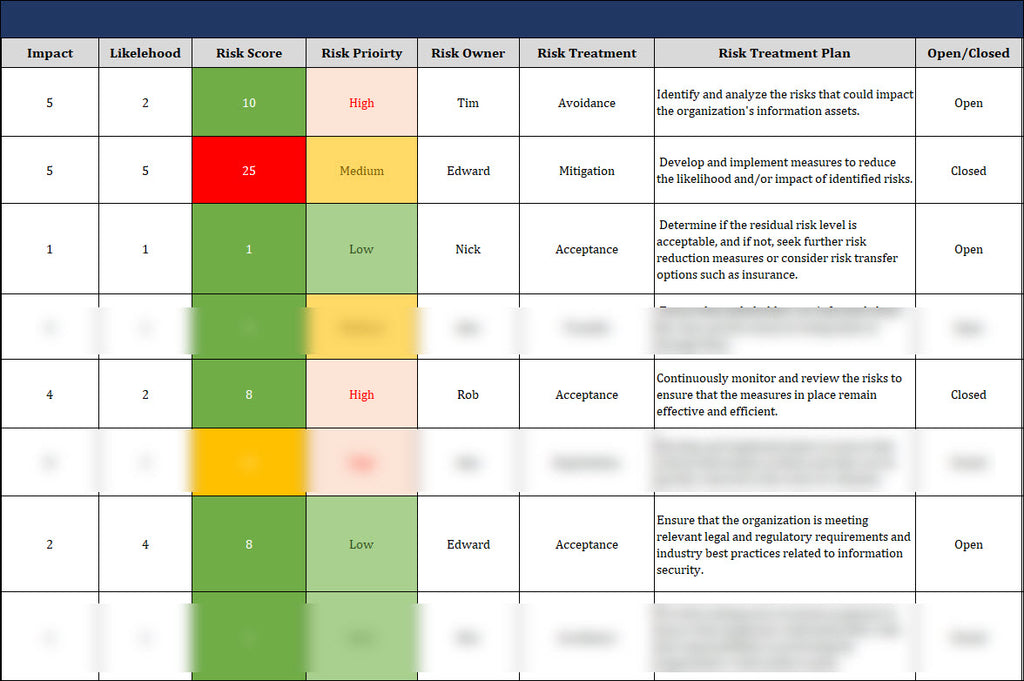
An information security risk register serves as an essential organizational tool for the identification, evaluation, and tracking of information security risks. Notably, the ISO/IEC 27001 standard mandates including an Information Security Risk Register within an organization's Information Security Management System (ISMS).
Significance of a Risk Register
- Risk registers serve as invaluable instruments for collecting data, aiding senior executives and operational teams in gaining a comprehensive understanding of their organization's critical risks and how to manage these risks to align with organizational objectives effectively. Consequently, any organization committed to maintaining a robust risk management process should not underestimate the pivotal role of constructing a risk register.
- Organizations should utilize the risk register to capture and distribute risk-related information across all company levels. This repository of information proves to be an essential resource for risk managers.
- A risk register can be seamlessly integrated into any risk management strategy an organization employs. Numerous resources delineate Enterprise Risk Management frameworks and processes, including established frameworks from organizations like the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations (COSO), Office of Management and Budget (OMB) circulars, and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
Guidelines for Maintaining a Risk Register
- After data has been entered into a risk register, the next step involves identifying recurring patterns in potential threats and system failures that may lead to adverse consequences.
- When opting for a risk register, it is essential to initiate a comprehensive discussion involving all relevant stakeholders to establish a consistent framework for evaluating risks, regardless of the diverse business divisions involved.
- The alignment of risk response decisions with corporate objectives and financial guidance, coupled with a deep understanding of specific risk data, empowers company leaders, bolstering their confidence in risk management choices.
- For risks under their jurisdiction, risk owners are responsible for accurately recording risk responses in the risk register. This necessitates thoroughly verifying risk reduction measures to ensure they align with the risk owners' expectations. Regularly assessing the relevance of specific protocols and the effectiveness of existing controls intended to mitigate risks is vital.
- Collaboration between risk owners and compliance or internal audit teams is crucial in discerning where risk management and compliance efforts intersect. Such collaborative processes provide decision-makers with a comprehensive view of their potential exposure, enabling them to effectively address strategic, operational, reporting, and compliance objectives.
- In the event of a significant incident within the organization, maintaining a risk register facilitates the preparation of enterprise-level risk disclosures required for mandatory submissions, hearings, and the production of formal reports.
Creating an Information Security Risk Register: Step-by-Step
- Risk Identification: Initiate the process by identifying the risks pertinent to the organization and classifying them based on their level of sensitivity. Following the initial creation of the register, it is imperative to conduct periodic reviews and make updates as necessary to account for alterations in the organization's assets, potential threats, and mitigation strategies.
- Enumerate Potential Risks: Once you've pinpointed your critical data and systems, list potential risks that could pose a threat. These risks may emanate from various sources, including cyber-attacks, natural disasters, human errors, or theft. To facilitate the brainstorming of potential risks, consider utilizing threat modeling tools such as ATAAPT (Attack Tree Analysis and Probabilistic Threat) or STRIDE (Spoofing, Tampering, Repudiation, Information Disclosure, Denial of Service).
- Assess Risk Criteria: It is essential to evaluate the potential downside of each risk. If the potential adverse consequences outweigh any potential benefits, the risk is generally deemed unworthy. Additionally, the likelihood of successful risk realization should be considered; if success seems improbable, the risk may not be worth taking. Finally, an assessment of risk tolerance is vital. If even a minimal risk is deemed unacceptable, it is advisable to refrain from taking that risk.
- Involve Stakeholders: Ensure all pertinent stakeholders are engaged in the process. This inclusivity helps guarantee that the risk register is comprehensive and that all parties are in alignment when it comes to responding to risks.
- Craft Risk Statements: A risk statement is an explicit declaration identifying potential risks to the organization. It should encompass a description of the event or circumstance, an outline of possible consequences, and an evaluation of the likelihood of the event occurring. Risk statements should be specific, measurable, and actionable.
- Specificity Matters: When detailing risks, be as specific as possible. Vague or incomplete information is of limited use when formulating effective risk responses.
- Ongoing Updates: Regularly update the risk register to accommodate new risks emerging and adapt to changing strategies for addressing existing risks.
- Relevance and Accessibility: Keep the risk register accessible to all relevant parties. This ensures that everyone can easily stay informed about the latest developments concerning information security risks.
Conclusion
Information Security Risk Register is a critical component for organizations seeking to establish a robust Information Security Management System (ISMS). This comprehensive tool enables systematic identification, assessment, and management of information security risks, fostering a proactive approach to safeguarding valuable assets.
The Risk Register, aligned with ISO 27001:2022 standards, provides a structured framework for organizations to prioritize risks, implement mitigation strategies, and continuously improve their information security posture. Its utilization is paramount in creating a resilient ISMS that adapts to evolving threats, demonstrating a commitment to maintaining the highest standards of information security in accordance with ISO 27001:2022.



