GDPR Response To Rectification of Data Request Template
Introduction
The GDPR guidelines brought to light the issue of the data subjects’ rights regarding knowing which of their data is being collected and how it’s being stored, protected, and used. Another by-product of this procedure is that the accuracy of the personal data stored by the organization must be the focus of the data controller. In case an inaccuracy becomes apparent, the data controller needs to make their best efforts to amend the inaccuracy. How this inaccuracy needs to be rectified must be clear to all the organizations’ employees, especially ones who have access to or use the personal data of the data subjects.
The rectification must be done within a reasonable timeframe, which should be documented in the organization’s GDPR charter. The DPO should oversee the maintenance of the timeframe and periodically update it.
When responding to the rectification request of a data subject, the DPO (or their delegates) must fill in certain fields, which are outlined in the “scope and purpose” paragraph below. The benefits of following a uniform process are ensuring that the data subjects’ data is accurate, tracking the rectification requests to their completion within a reasonable timeframe, and consistency in the responses.
Scope and Purpose
There are two triggers to creating a response: A specific request from a data subject or their proxy or if the data inaccuracy becomes readily apparent. Once either trigger has occurred, the data controller needs to respond to the request while using the organization’s process, which the DPO has created. The response must be in readable everyday language and should be kept readily available for any internal or external audits.
Once a rectification request has been submitted, the data controllers are required to:
1. Check that the personal data mentioned exists on the organization’s servers and that it’s as described in the request.
2. If it is, validate that the data subject (the requester) is indeed the owner of the data or a proxy of the legitimate end-user.
3. If they are, correct the data as requested and send a confirmation of the correction.
4. If it hasn’t (either point #2 or #3), Inform the data subject (the requester) that
their request can’t be resolved, along with an explanation as to why.
5. Keep a record of the request, its response, and any further communication with the requester. This is required for the audits.
The Obligations of the Data Controller
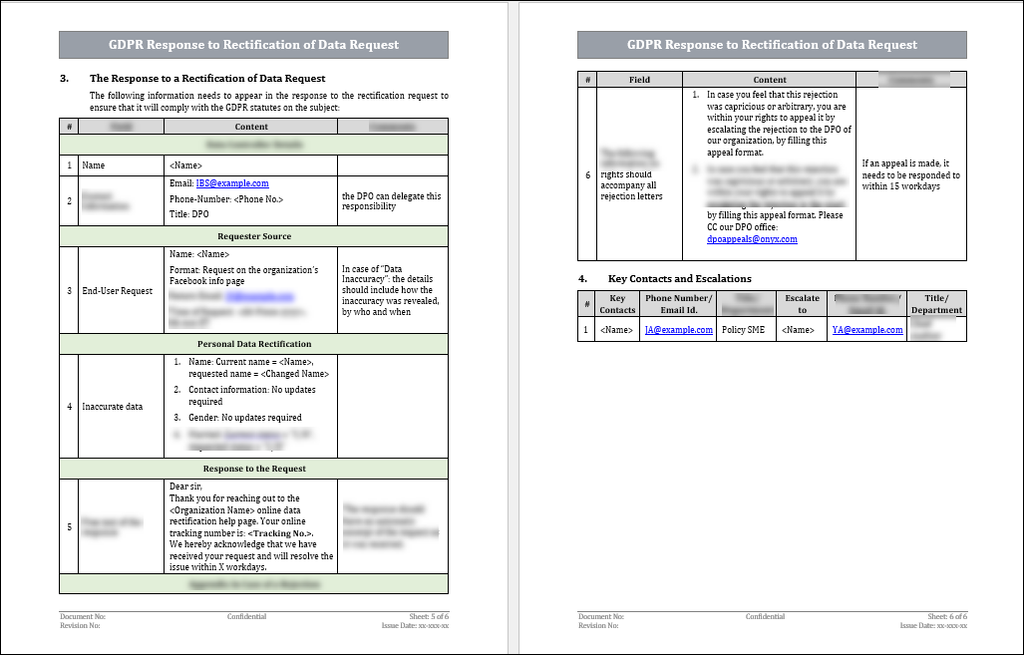
The rectification response should include the following fields:
1. The details of the DPO or their delegate (or data controller)
2. The source of the request: either the inaccuracy or the data subjects’ request.
3. Which attributes of the personal data need to be rectified?
4. The response to the request.
5. In case of rejection: Inform the data subject of their right to escalate the request to the GDPR supervisory authority of the country to enforce their request.
Other Obligations -
1. Establish that data subjects’ (the requesters’) personal data is collected and stored.
2. Make sure that the request is understood and that the data is updated as requested.
3. Send proof that the rectifications were made to the data subject (the requester)
Examples of Processed Personal Data
Attributes -
1. Name
2. Phone number
3. Email address
4. IP address
5. ID number
6. Marital status
7. Number of children
8. Annual income
9. Political opinions
10. Religious beliefs
11. Sexual orientation
Term Definitions
What is a Data Controller?
An organization or person who determines the use of the collected personal data from the data subjects. The data controller owns the collected personal data, decides in which ways it will be processed, and bears the sole responsibility for safekeeping it.
What is personal data?
Any type of unique data which relates to an individual data subject. This can include such information as Name, phone number, Email address, ID number, health records, political opinions, IP address, etc.
What is the processing of personal data?
Any act that is performed on the collected personal data of all the organizations’ data subjects. This may include such actions as storing the data, analyzing it to extract insights, or deleting it once it is no longer required.
What is a data subject (also known as an end-user)?
Any person who created a unique username on the organization’s website, thus giving them the possibility of using that username to perform certain tasks and use features offered on the website.
Who is the DPO?
The Data Protection Officer is the main stakeholder of the organization for all aspects of GDPR compliance. They are responsible for making sure that the GDPR guidelines are adhered to.
What is a data breach?
Any intentional or unintentional security incident which involves the sharing of personal data with any unauthorized element. Sharing of personal data may include the viewing, copying, stealing, or altering of the personal data.
Key Takeaways / Conclusions
1. The DPO (or their delegate) is responsible for checking the restriction request and responding to it.
2. Since some time usually passes between the submission of the request and the response to it, The response should have an automatic excerpt of the data subject’s request.
3. In the case of “Data Inaccuracy,” the details should include how the inaccuracy was revealed, by whom, and when.
4. If an appeal is made by the data subject, it needs to be responded to within 15 work days.
5. All rectification must be done on all the organizations’ servers, both the primary and secondary (disaster recovery)


