GDPR Response on Processing Restriction Request-Complaint Template - Accepted
Introduction
Under the GDPR guidelines, any individual who is a data subject has the right to request that the organization that collects and processes their personal data restrict their processing. When this request is submitted, the data controllers must respond promptly while using clear everyday language. In case the restriction request is accepted, the data controller is required to inform the data subject of the implication of their request and when it will be implemented.
The DPO or their delegates need to respond to the request of the data subject to comply with the GDPR statutes regarding the restriction request of processing of any personal information which belongs to the organizations’ data subjects. After the consent form has been signed by the data subject, the data controllers are within their rights to process any personal data collected from them. The GDPR stipulates that the data subjects are entitled to ask to withdraw the consent form, however the organization are sometimes within their rights to reject this request.
The filled-in request must be kept in the organization's archive for audit purposes.
Scope and Purpose
GDPR processing restriction request is a request made by end users for restricting the process of their personal data by a data controller. The organization may reject the processing restriction request if one of the following occurs:
1. If the end user contested the accuracy of the personal data, but that was found to be unsubstantiated.
2. The processing of the personal data is lawful, as opposed to what the end-user claimed.
3. The organization has verified legitimate grounds for overriding the restriction request.
4. The processing of the personal data is required for legal proceedings.
5. If none of the above are relevant to the request, then the data controller is required to comply in a timely manner.
According to the GDPR: Once a processing restriction request has been submitted, the data controllers are required to -
1. Make an effort to comply with the request.
2. Check that the personal data mentioned exists on the organization’s servers, and that it’s as described in the request.
3. If it is, Validate that the requester is indeed the owner of the data or is a proxy of the legitimate end-user.
4. If they are, Check if the organization has any reason not to comply with the request.
5. If row 3 is negative, Inform the requester that their request is valid and will be processed promptly.
6. Keep a record of the request, its response, and any further communication with the requester. This is required for audits.
The Obligations of the Data Controller
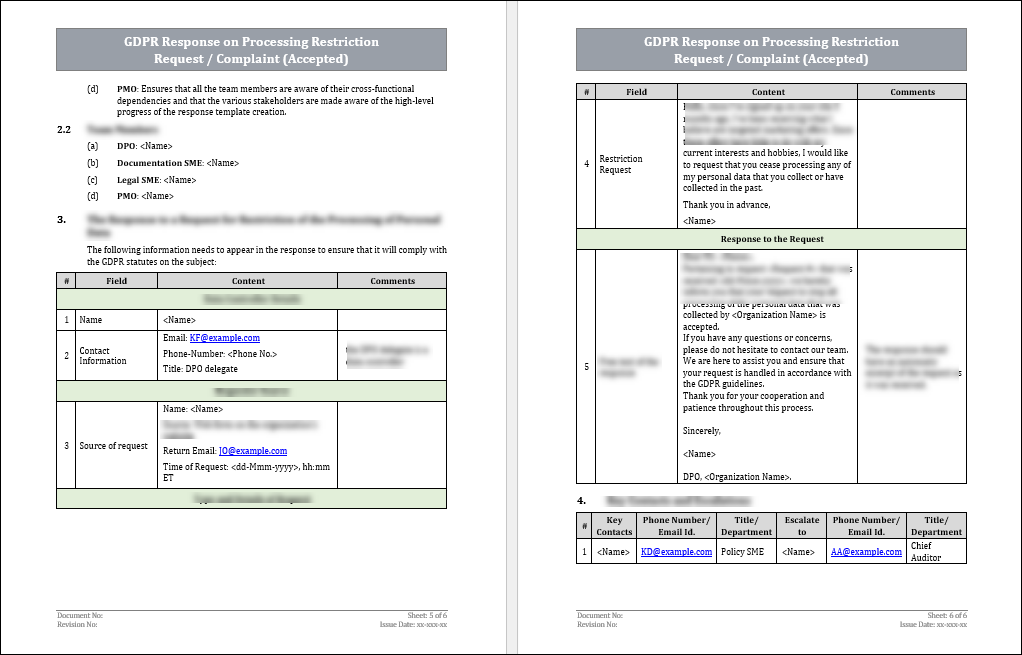
The rectification response should include the following fields -
1. The details of the responder (or data controller).
2. The basic details of the requester.
3. Which processing of the personal data was requested to be restricted.
4. The response to the request.
Other Obligations -
1. Establish that the requesters’ personal data is processed in any way.
2. Ascertain that the request is feasible, and if not, explain why.
3. Notify the requester of the decision that the organization intends to comply with their request.
4. To securely store the personal data of the data subjects, both on the primary and secondary servers of the organization.
5. Restrict the access to personal data to only those who need it and who are authorized to do so.
6. Not process the personal data for marketing purposes or sell it to third-party organizations for the same purposes.
7. Not transferring personal data to third parties without the data subject's consent.
8. Sensitive Data: Where the transfer involves personal data revealing racial or ethnic origin, political opinions, religious or philosophical beliefs, or trade union membership, genetic data, or biometric data for the purpose of uniquely identifying a natural person, data concerning health or a person’s sex life or sexual orientation, or data relating to criminal convictions and offences (hereinafter “sensitive data”), the data importer shall apply specific restrictions and/or additional safeguards. E.g.: Masking data.
Term Definitions
What is a Data Controller?
An organization or person who determines the use of the collected personal data from the data subjects. The data controller owns the collected personal data, decides how it will be processed and bears the sole responsibility for safekeeping it.
What is personal data?
Any type of unique data which relates to an individual data subject. This can include such information as: Name, phone number, Email address, ID number, health records, political opinions, IP address, etc.
What is the processing of personal data?
Any act that is performed on the collected personal data of all the organizations’ data subjects. This may include such actions as storing the data, analyzing it in any way to extract insights or deleting it once it is no longer required.
What is a data subject (also known as an end-user)? Any person who created a unique username on the organization’s website, thus giving them the possibility of using that username to perform certain tasks and use features offered on the website.
Who is the DPO?
The Data Protection Officer is the main stakeholder of the organization for all aspects of GDPR compliance. They are responsible for making sure that the GDPR guidelines are adhered to.
What is a data breach?
Any intentional or unintentional security incident which involves the sharing of personal data with any unauthorized element. Sharing of personal data may include the viewing, copying, stealing, or altering of the personal data.
Key Takeaways / Conclusions
1. The DPO (or their delegate) is responsible for checking the restriction request.
2. Since some time usually passes between the submission of the request and the response to it, The response should have an automatic excerpt of the data subject’s request.
3. The response should have an automatic excerpt of the request as it was received by the data subject.


