GDPR Response on Consent Withdrawal - Restriction Request Template - Rejected
Introduction
The shift of power in favour of the data subjects was one of the main benefits of the GDPR. However, it didn’t place all the power in their hands. The organization which collects their personal data does sometimes have the right to refuse to erase (partially or wholly) the data subject’s personal data. There are several exceptions to the rule, saying that once a withdrawal or restriction request has been submitted, it must be adhered to.
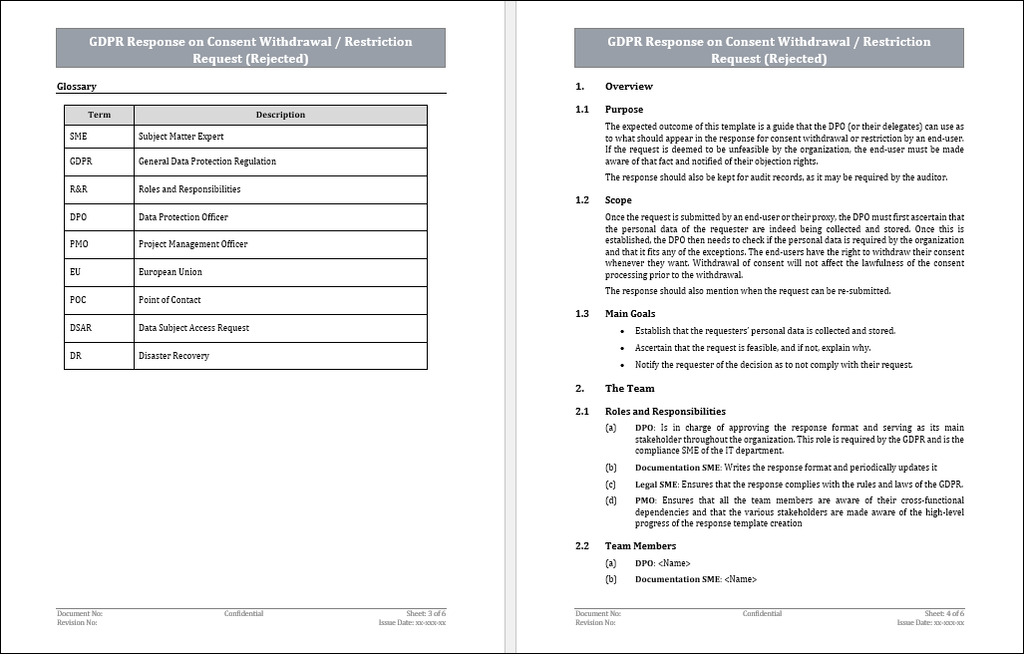
The DPO (or their delegates) need to respond to the consent withdrawal or restriction by a data subject. If the request is deemed unfeasible by the organization, the data subject must be made aware of that fact and notified of their objection rights. The response should also be kept for audit records, as it may be required by the auditor.
The following reasons allow the organization to reject the request -
1. The processing of the data may assist in the prevention or detection of a crime.
2. The processing of the data may assist in the prosecution of offenders.
3. The processing of the data is in the best interest of the public, e.g., Health concerns.
4. The processing of the data is required under law, e.g., Tax laws.
Scope and Purpose
Once the request is submitted by an end-user or their proxy, the DPO must first ascertain that the personal data of the requester are indeed being collected and stored. Once this is established, the DPO then needs to check if the personal data is required by the organization and that it fits any of the exceptions. The end-users have the right to withdraw their consent whenever they want. Withdrawal of consent will not affect the lawfulness of the consent processing prior to the withdrawal. The response should also mention when the request can be re-submitted.
Once a withdrawal/restriction request has been submitted, the data controllers are required to -
1. Check that the personal data mentioned exists on the organizations’ servers and that it’s as described in the request.
2. If it is, Validate that the requester is indeed the owner of the data or a proxy of the legitimate end-user.
3. If they are, Check if the organization has any reason not to comply with the request.
4. If row #3 is positive, Inform the requester that their request can’t be resolved, along with an explanation as to why.
5. Keep a record of the request, its response, and any further communication with the requester. This is required for audits.
The Obligations of the Data Controller
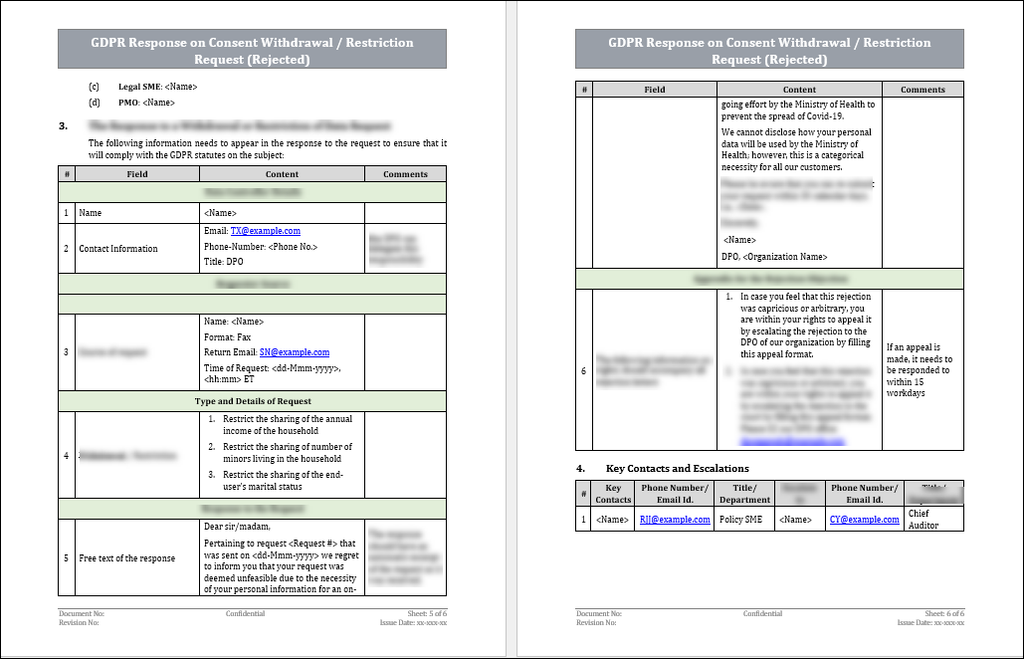
The restriction response should include the following fields -
1. The details of the responder (or data controller)
2. The basic details of the requester.
3. Which attributes of the personal data were requested to be erased (withdrawal or restriction)
4. The response to the request.
5. In case of a rejection, Inform the end-user of their right to escalate the request to the courts of the country to enforce their request.
Other obligations -
1. If the request is made by a proxy of the data subject, Establish that the requester’ is the legal guardian of the data subject.
2. Explain the reason for rejection in clear, everyday language.
3. Notify the requester of the decision as to not comply with their request.
Term Definitions
What is a Data Controller?
An organization or person who determines the use of the collected personal data from the data subjects. The data controller owns the collected personal data, decides in which ways it will be processed and bears the sole responsibility for safekeeping it.
What is personal data?
Any type of unique data which relates to an individual data subject. This can include such information as: Name, phone number, Email address, ID number, health records, political opinions, IP address, etc.
What is the processing of personal data?
Any act that is performed on the collected personal data of all the organizations’ data subjects. This may include such actions as storing the data, analyzing it in any way to extract insights or deleting it once it is no longer required.
What is a data subject (also known as an end-user)?
Any person who created a unique username on the organization’s website, thus giving them the possibility of using that username to perform certain tasks and use features offered on the website.
Who is the DPO?
The Data Protection Officer is the main stakeholder of the organization for all aspects of GDPR compliance. They are responsible for making sure that the GDPR guidelines are adhered to.
What is a data breach?
Any intentional or unintentional security incident which involves the sharing of personal data with any unauthorized element. Sharing of personal data may include the viewing, copying, stealing, or altering of the personal data.
How To Communicate With Data Subjects?
The data subject may submit their request by any number of communication means -
1. Email: send the request to the data controller using a dedicated Email address.
2. Website: Opening a request (also known as a ticket) on the data controllers’ site.
3. Mail: Sending a filled-in form in an envelope.
The data controller is obligated to respond to the request using the same means of communication. The response needs to explain why the request was rejected and explain that the data subject has the right to appeal the decision to the GDPR supervisory authority.
Key Takeaways / Conclusions
1. The DPO (or their delegate) is responsible for checking the restriction request and explaining why it was rejected.
2. The response should have an automatic excerpt of the data subject’s request.


